Defination:-
Removal of limb, partly or totally, from the body, is termed as Amputation. Disarticulation is removing the limb through a joint.
Indication:-
Level of Amputation:-
In a limb, an amputation is carried out at a level which will give the stump an optimum length to facilitate prosthetic fitting. The level of amputation is determined by the viability of the tissues. However, it is important that the stump should have a well-healed, non tender, supple scar.
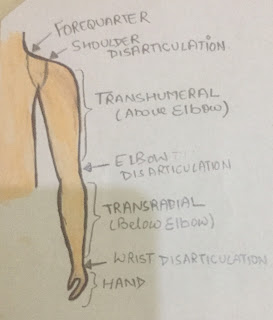
UPPER EXTREMITY
👉 Forequarter amputation - Also known as scapulothoracic amputation. It is carried out proximal to the shoulder joint. In this type of amputation, part of scapula and clavicle are removed along with the shoulder girdle muscles.
👉 shoulder disarticulation- It is the removing of shoulder joint, but is generally not so popular.
👉 Above- elbow amputation- Also known as Transhumeral amputation. A 20-cm-long stump from the tip of the acromion is measured.
👉 Below-elbow amputaion- Also known as Transradial amputation. The optimum length of the stump is 20cm from the tip of olecranon.
👉Krunkenberg amputation:- In this, the forearm is split between the radius and ulna to provide the pincer grip. The patient can hold a spoon or lighter objects with this 'fork'. 'Hook' prosthesis can be put over this stump for cosmetic purpose.
👉Amputation through the hand:- In this, many forms of amputation are performed through the hand i.e. through metacarpals, etc.
LOWER EXTREMITY
👉 Hindquarter amputation:- Also known as Transpelvic amputation. In this, part of pelvis is removed along with the lower extremity.
👉 Hip disarticulation:- The femur is removed from the acetabulum is performed.
👉 Above knee amputation:- Also known as transfemoral amputation. The optimum length of the stump is about 25-30 cm measured from the tip of the greater trochanter.
👉Knee disarticulation:- It can be performed through the knee as well but not acceptable cosmetically.
👉Below knee amputation:- Also known as transtibial amputation. It is most commomly performed amputation. In this, the optimum length is 14 cm from the tibial tubercle. A patellar tendon bearing (PTB) prosthesis can be fitted over the stump of adequate length.
👉Syme's amputation:- In this operation, the tibia and fibula are divided just above the ankle joint then the skin over the heel is attached back to the stump end of the stump with or without calcaneum.
PHYSIOTHERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT OF THE AMPUTEE
Physiotherapy plays the most significant role in the management of an amputee from the time the surgeon decides for amputation till the patient is back to his work.
The basic approach of physiotherapy is to establish a new proprioceptive system.
The management is divided into three stages:-
i) Preoperative stage
ii) Early postoperative stage
iii) Mobility stage
1. preoperative stage:-
Assessment:- The physiotherapist has to assist the ROM, muscle power, Condition of the skin, status of circulation and sensation, the status oh hearing and vision.
:- Assessment of the psychological status is extremely important as losing a limb can produce psychological trauma which can lead to depression.
:- besides these, it is also important to know the environment of the patient's home and his working place.
Preoperative training:- The aim of the preoperative training is to prevent the complications of the postoperative phase.
:- teach breathing techniques, isometrics of the muscles, positioning and mobility, balance, equilibrium,walking techniques.
:- the patient should also be educated to take care of the pressure points and about the phantom pain
Reassurance:- Psychological reassurance can be done by practical demonstration by the patient who has undergone same surgery.
2. Early postoperative stage:-
☺Breathing exercises which were taught preoperatively are done to prevent any chest complications.
☺There are more chances of developing contracture (adduction and rotation) so to prevent this, the patients limb should be positioned correctly all the time i.e. any position which can develop contracture should be avoided.
☺The patient should be encouraged to move in the bed by pushing up the body on the arms. Vigorous ROM and strengthening exercises should be given for whole body.
After 3-4 days of surgery, the stump exercises can be initiated in pain free range.
Management of the stump
TO CONTROL STUMP OEDEMA
Stimulation with limb in elevation with the elastic bandage.
Resistive exercises to the stump and the rest of the joints.
Stump bandaging and conditioning play an important role in conditioning and shaping of the stump.
PRINCIPLES OF BANDAGING THE STUMP
The pressure of the bandage should be moderatively firm and evenly distributed, decreasing proximally. Extra pressure is necessary over the corners to obtain a conical shape of the stump.
STUMP HYGIENE
The regular washing of the stump with warm disinfected soap water and thorough drying.
3. Mobility stage:-
This is the stage of mobilisation and restoration of functional independence.
It starts with crutch walking. (It has been observed that patient tend to walk on crutches holding the stump in flexion, it should be avoided.)
Walk in parallel bar with both arm support ↣ ↣ ↣ ↣ Walk in parallel bar with one hand support








No comments:
Post a Comment