INTRODUCTION
* It is unusual for a specific lung function test to diagnose a disease. A series of tests may be done to diagnose the lung disorder to one of several categories and when other features such as history, physical examination, radiology and pathology are added, a complete/possible diagnosis is considered.
AIMS OF PFT
💧 to define more clearly the type of functional disorder.
💧 to measure the progression or regression of the disorder.
💧 to decide the feasibility of thoracic surgery
💧to assess the degree of respiratory failure.
CLASSIFICATION OF PULMONARY DISEASE ACCORDING TO THE PFT
The PFT provides the basic classification of pulmonary disease into three major pathological categories:
i) OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASE:- When there is any obstruction in the airways. It is characterised by decreased forced expiration.
ii) RESTRICTIVE LUNG DISEASE:- It is characterised by decreased lung volumes.
iii) COMBINED LUNG DISEASE:- It involves both i.e. decreased inflow and lung volumes.
PARAMETERS OF PFT
i) measurement of lung size.
ii) measurement of ease of flowing of air in and out of the lungs
iii) measurement of efficiency of gaseous exchange process.
CATEGORIES OF PFT
i) Ventilatory Function Test
ii) Arterial Blood Gas analysis/ Test for gaseous exchange
iii) Exercise Tolerance Test
1. VENTILATORY FUNCTION TEST
A spirometer is used for testing the ventilatory of an individual. The patient is asked to breathe in as far as he/she can and breathe out maximally as possible. This volume of air is called the vital capacity. The vital capacity when measured by the spirometer in which the deepest breathe in is followed by forced breathe out is called Forced Vital Capacity.
The maesure of vital capacity and FVC gives an indication of the ventilatory capacity of the lungs.
In normal individual the VC and FVC are approximately equal. But in case of COPD, the compression of the airways during forced expiration causes an earlier closure of airway
in COPD, FVC<VC
The volume of air that can be breathe out during a forceful expiration in 1st second is called FEV1 (Forced Expiratory Volume in 1st second). Normally, the FEV1 is 70% of FVC. In case of COPD, expiration is prolonged and so that ratio of FEV1/FVC is decreased. In restricted lung disease, there is a restriction in lung expansion but no effect on the airways. So, FEV1 and FVC are reduced but their ratio remains normal.
Spirometer
2. ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS ANALYSIS
OR
TEST OF GAS EXCHANGE
For efficient respiratory gas exchange, the major process of lung ventilation, diffusion across the alveolar-capillary membrane and lung perfusion should be intact. We check it by ABG analysis (Arterial Blood Gas analysis).
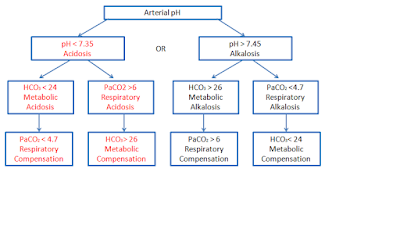
ABG analysis is an essential part of diagnosis and managing of patient oxygenation status and acid-base balance. The pH is the measurement of the "acidity" and "alkalinity" of blood. It is inversely proportional to the number of H+ ions in the blood. It means more the H+ ions, less will be the pH and vice versa. The pH is measured on the scale from 1-14. The normal blood pH is 7.35-7.45, in order for normal metabolism to take place, the body must maintain this narrow range all time. Below 7.35, the blood is acidic and above 7.45, the blood is basic or alkaline.
*significant changes in blood above pH 7.8 or below 6.8 will interfere with cellular functioning and if it is uncorrected it will lead to death.*
RESPIRATORY BUFFER RESPONSE:- A normal biproduct of cellular metabolism is CO₂. CO₂ is carried in the blood to lungs where excess CO₂ combines with water to form carbonic acid H₂CO₃. The blood pH will change according to level of carbonic acid present. This triggers the lung either to increase or decrease the rate and depth of the ventilation until the appropriate amount of CO₂ has been establish. Activation of lungs to compensate for balance starts within 1-3 minutes.
RENAL BUFFER RESPONSE:- In an effort to maintain the pH of blood within its normal range, kidney excretes or retain bicarbonate. As the blood pH decreases the kidney will compensate it by retaining bicarbonate and as the pH rises the kidney excretes bicarbonate ions through the urine. This provides an excellent means of regulating acid-base balance. The system may take from hours to days to correct the imbalance.
* When respiratory system and renal system are working together they are able to keep blood pH balanced.
ACID-BASE DISORDERS
💧 Respiratory acidosis
💧 Respiratory alkalosis
💧 Metabolic acidosis
💧 Metabolic alkalosis
RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS
It is defined as a pH less than 7.35 with PaCO₂ greater than 45mmHg. Acidosis is caused by an accumulation of CO₂ which combines with water in the body to produce carbonic acid thus lowering the pH of blood. RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS
It is defined as a pH > 7.45 with PaCO₂ < 35mmHg. Any condition that causes hyperventilation can result in respiratory alkalosis.
METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
It is defined as a bicarbonate level < 22meq/l with the pH < 7.35.
METABOLIC ALKALOSIS
It is defined as the bicarbonate level > 26meq/l with pH > 7.45.
3. EXERCISE TOLERENCE TEST
Spirometry alone cannot predict about how much a person can walk.Nor the asking the patient is reliable. Hence ETT can give an accurate assessment. As walking can affect our cardiopulmonary system, so this test can assess these functions.
So, ETT is used to assess the patients capacity to tolerating breathing intensity of exercise while ECG, B.P., Heart rate and symptoms re monitored for the evidence of myocardial ischemia, abnormal electrical conduction or other abnormal sign and symptoms of congestion.
TYPES OF TESTS:- Treadmill test, six-minute walk test, cycle ergometer, upper limb ergometer, stairs climbing.
PROCEDURE:- Before exercising, the patient is hooked up to EKG machine. The patient is required to exercise at progressively greater impedence of work while increase of the speed and grade of treadmill or increase the speed and resistence to padelling the extremity on bicycle ergometer.
ABSOLUTE INDICATION OF TERMINATING ETT:-
💧 Systolic B.P.> 10 mmHg than the baseline.
💧 moderate to severe angina
💧 neurological problems like ataxia or dizziness
💧 cynosis or pallor
RELATIVE INDICATION OF TERMINATING ETT:-
💧 fatigue
💧 shortness of breath
💧 wheeze
💧 B.P. ( systolic >200, Diastolic < 110)









No comments:
Post a Comment